Current
Electricity Saving Special Part 1: the most important facts about electricity consumption
Saving electricity is the big topic in the fall/winter of 2022/23.
Have you ever wondered which are the biggest power guzzlers in your household and which appliances and habits are actually the easiest and most energy-saving?
If you’re like many others, you’ve come to the right place. We have put together a simple and easy-to-understand series for you on the subject of saving electricity and would like to provide you with all the important information as simply and comprehensibly as possible.
In the first part of the series on saving electricity, we explain how electricity is measured and calculated and show you simple calculation examples with typical devices that can certainly be found in your household.
In the end, you will understand how electricity usage is reported on your electric bill and how each appliance affects your electricity costs.
The better you know your electricity consumption, the better you can save electricity
Saving electricity is on everyone’s mind this fall and winter. This has been the case at least since the Federal Council launched its campaign “Energy is scarce. Let’s not waste it.” has launched.
The truth is, many of the really effective measures to save electricity can no longer be implemented in the short term. But still, with a few tricks that involve little to no sacrifice, it may be possible to save well over CHF 100 in annual electricity costs.
Therefore, you should also know the most important basics about saving electricity. In this article you will learn the following:
- How the power consumption of devices is measured/calculated
- Which are the biggest power guzzlers in the household
- How much electricity an average household in Switzerland consumes
- How to find out your own power consumption
- What electricity will cost in Switzerland in 2022 and 2023
- How you can save a lot of electricity and money on electrical appliances with little sacrifice
How is electricity consumption measured or calculated?
In order to address the issue of saving electricity, you should be aware of the impact that the appliances in your home have on your electricity bill in the first place. The power consumption differs greatly between different devices.
To do this, it is advisable to know how to calculate the power consumption of devices.
Calculate electricity consumption: Watt and kilowatt hour
To calculate the power consumption of a particular device, you need to know its power. This is specified for each electronic device and is measured in watts (W).
The more watts, the higher the electrical power of a device, the more electricity it consumes
Of course, the power consumption of the device also depends on how long the device is in operation. If you bring the time factor into play, you are talking about kilowatt hours (kWh).
Power consumption in kWh = wattage of the device x time (duration of use in hours)
Example calculation OLED TV (55″)* with Swisscom TV Box
- Power consumption OLED TV and Swisscom TV Box = 305 W
- Average daily usage time = 4 hours
305 W x 4 h x 365 days = 438 kWh
The example calculation shows that our daily 4-hour TV consumption consumes about 438 kWh of electricity per year. With an average electricity price in Switzerland in 2022 of 21.2 centimes, this results in electricity costs for TV consumption of around CHF 93.
* The power consumption of modern OLED and LED TVs depends heavily on the brightness settings. The backlight of the screen has the biggest impact on its power consumption. The same goes for devices like smartphones, tablets, monitors, etc.
Example calculation power consumption desktop PC with 24 inch monitor
- Power consumption desktop PC and monitor = 250 W
- Average daily usage time in home office = 8 hours
- Average annual working days = 225
250 W x 8 h x 225 days = 450 kWh
The example calculation shows that our home office consumes about 450 kWh of electricity per year. With an average electricity price in Switzerland of 21.2 centimes in 2022, this results in electricity costs for the home office of around CHF 95.
Example calculation of electricity consumption air conditioner (installed split unit)
- Power consumption air conditioner = 1’000 W
- Average daily usage time = 12 hours
- Average annual operating days = 60
1’000 W x 12 h x 60 days = 720 kWh
The example calculation shows that a fixed installed air conditioner consumes about 720 kWh of electricity per summer. With an average electricity price in Switzerland in 2022 of 21.2 centimes, this results in electricity costs for the air conditioning system of about CHF 153. Mobile monobloc air conditioners still consume about 25% more electricity than permanently installed split units.
Example calculation electricity consumption oven
- Oven power consumption per baking cycle = 1 kWh
- Baking operations per year = 100
1 kWh x 100 = 100 kWh
The example calculation shows that our oven consumes about 100 kWh of electricity for an average of 100 baking processes per year. With an average electricity price in Switzerland in 2022 of 21.2 centimes, this results in electricity costs for the oven of about CHF 21.
How to find out your own power consumption
You will see the total amount of electricity consumed in your household on your annual electricity bill at the latest. On the bill you will be able to read the electricity consumption in kilowatt hours (kWh), on the basis of which the cost of the consumed electricity will be calculated.
If you want to know the exact and effective power consumption of a particular device, you can measure it with an ammeter. These meters are simply plugged between the socket and the electrical appliance.
Electricity meters can often be borrowed free of charge from your local energy supplier, check directly with your electricity supplier.
For example, rent electricity meter in Zurich.
The biggest power guzzlers in your household
Breakdown of typical household electricity consumption in 2019
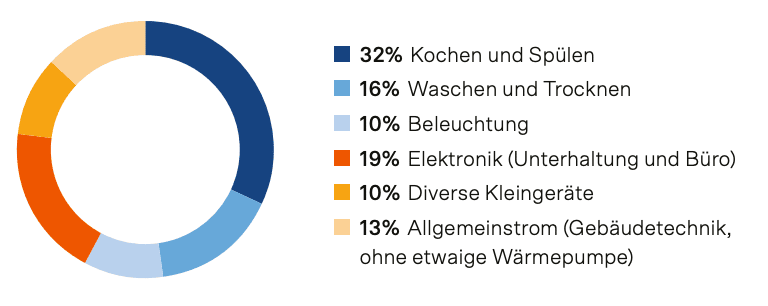
Comparison power consumption of typical household appliances
| Device | Watt |
| Electric stove (glass ceramic) | 3000 |
| Oven (200 degrees) | 1000 – 2000 |
| Tumble dryer | 3000 |
| Dishwasher | 2300 |
| Washing machine (6kg) | 2000 |
| Kettle | 2200 |
| Hair dryer | 2000 |
| Vacuum cleaner | 1500 |
| Air conditioner (Installed split unit) | 1000 |
| Microwave | 800 |
| Nespresso coffee maker | 1300 |
| Extractor hood | 400 |
| Refrigerator | 120 |
| Freezer | 150 |
| PC (desktop) | 200 |
| PC Monitor (24 inch) | 50 |
| Notebook | 80 |
| Light bulbs | 40 – 60 |
| LED illuminant | 2 – 8 |
| OLED TV (55″) (max. brightness and HDR) | 300 |
| LED TV (55″) | 150 |
| TV Box (e.g. Swisscom Box 21) | 5 |
With the values from the table above, you can quickly see which are the biggest power guzzlers in the house and where the most electricity can be saved. Of course, the duration or frequency with which the equipment is used plays a major role.
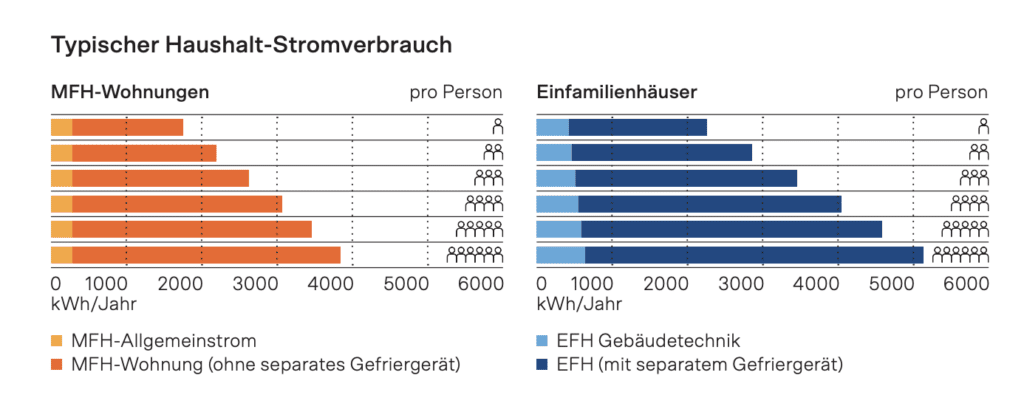
Annual electricity consumption and electricity costs of an example household in Switzerland in 2022
| Device | Usage time per day or number per year | kWh/year | Electricity costs 2022 (CHF/year) |
| Electric stove (glass ceramic) | 1 h/day | 1095 | 232 |
| Oven (200 degrees) | 100 baking processes | 100 | 21 |
| Tumble dryer | 160 dryer aisles | 320 | 68 |
| Dishwasher | 365 Washes | 274 | 58 |
| Washing machine (6kg) | 220 washing cycles (with different programs) | 160 | 34 |
| Kettle | 10 min/day | 136 | 29 |
| Hair dryer | 10 min/day | 124 | 26 |
| Vacuum cleaner | 10 min/day | 93 | 20 |
| Air conditioner (Installed split unit) | 12 h/day (60 days a year) | 720 | 153 |
| Microwave | 10 min/day | 50 | 11 |
| Nespresso coffee maker | 10 cups/day (3 min per cup = 30 min/day) | 237 | 50 |
| Extractor hood | 1 h/day | 146 | 31 |
| Refrigerator (Energy efficiency class 2021 E) | 24 h/day | 115 | 24 |
| Freezer (Energy efficiency class 2021 E) | 24 h/day | 200 | 42 |
| PC (desktop) | 4 h/day | 300 | 64 |
| PC Monitor (24 inch) | 4 h/day | 75 | 16 |
| Notebook | 4 h/day | 120 | 25 |
| Light bulb | 4 h/day | 60 – 90 | 13 – 19 |
| LED illuminant | 4 h/day | 3 – 12 | 1 – 3 |
| OLED TV (55″) | 4 h/day | 440 | 93 |
| LED TV (55″) | 4 h/day | 220 | 47 |
| TV Box (e.g. Swisscom Box 21) | 4 h/day | 10 | 2 |
| Total | 4’958 | 1’051 |
A quick glance at the table quickly reveals the biggest power guzzlers in the household.
In summary, in 2022, our example household falls:
- A total of CHF 900 in electricity costs for household and electrical appliances to
- Almost CHF 500 for cooking, baking, washing up, refrigerating and freezing food on
- Over CHF 150 in just one summer for air conditioning to
- Approximately CHF 60 for daily 4-hour TV consumption at
- About CHF 100 for washing and drying clothes to
In addition, there may be other large consumption items such as electricity consumption for heating (heating pumps, heating burners for oil heating), hot water preparation, light bulbs in outdoor lighting, electric cars, etc. These electricity consumptions account for another average of about 15% of the total electricity consumption and have not been included in our tables.
Appliances that are rarely found in a typical household, such as an aquarium, waterbed, gaming computer with continuous operation or dehumidifier, were also not included.
Annual electricity consumption and electricity costs of an example household in Switzerland in 2023
| Device | Usage time per day or number per year | kWh/year | Electricity costs 2023 (CHF/year) |
| Electric stove (glass ceramic) | 1 h/day | 1095 | 295 |
| Oven (200 degrees) | 100 baking processes | 100 | 27 |
| Tumble dryer | 160 dryer aisles | 320 | 86 |
| Dishwasher | 365 Washes | 274 | 74 |
| Washing machine (6kg) | 220 washing cycles (with different programs) | 160 | 43 |
| Kettle | 10 min/day | 136 | 37 |
| Hair dryer | 10 min/day | 124 | 33 |
| Vacuum cleaner | 10 min/day | 93 | 25 |
| Air conditioner (Installed split unit) | 12 h/day (60 days a year) | 720 | 194 |
| Microwave | 10 min/day | 50 | 13 |
| Nespresso coffee maker | 10 cups/day (3 min per cup = 30 min/day) | 237 | 64 |
| Extractor hood | 1 h/day | 146 | 39 |
| Refrigerator (Energy efficiency class 2021 E) | 24 h/day | 115 | 31 |
| Freezer (Energy efficiency class 2021 E) | 24 h/day | 200 | 54 |
| PC (desktop) | 4 h/day | 300 | 81 |
| PC Monitor (24 inch) | 4 h/day | 75 | 20 |
| Notebook | 4 h/day | 120 | 32 |
| Light bulb | 4 h/day | 60 – 90 | 16 – 24 |
| LED illuminant | 4 h/day | 3 – 12 | 1 – 3 |
| OLED TV (55″) | 4 h/day | 440 | 118 |
| LED TV (55″) | 4 h/day | 220 | 59 |
| TV Box (e.g. Swisscom Box 21) | 4 h/day | 10 | 3 |
| Total | 4’958 | 1’336 |
According to the Swiss Federal Electricity Commission, average electricity prices in Switzerland are set to rise by 27% in 2023. Locally, however, these price increases can vary widely.
In our example household, electricity costs would increase from CHF 898 in 2022 to CHF 1,142 in 2023.
Saving electricity with electrical appliances: What you need to know
A glance at the tables is enough to see that a lot of electricity can be saved quickly, especially in NPPs, namely in the:
- Cooking
- Cooling
- Washing
The energy-saving tips for electrical appliances from the Swiss Federal Office of Energy confirm this.
We are of the opinion that some tips bring only little and are nevertheless connected with much expenditure or renunciation. This is especially true in comparison to the really effective measures such as the Turn down the heating (1 degree cooler in the house reduces heating energy consumption by about 10%) or the Replacing old electrical appliances through newer and more energy-efficient technologies, such as energy-saving light bulbs (savings potential over 80%) or electrical appliances with higher energy efficiency (know and consider energy labels).
But there are also very effective tips, which show a great effect with little sacrifice.
Our top tips for saving electricity
Cooking
- If possible, the oven should be used with the convection function, this can save up to 15% electricity. If this is not possible, the convection function should be used at least for preheating and only then switched to top and bottom heat.
- If possible do not preheat oven, usually does not bring much and consumes up to 20% more electricity.
- Always bring water to a boil in the kettle and only then add to the pan.
- If possible, cook with a lid (not recommended for all dishes) and use pans of the right size.
- Replace old electric stove (stove with cast iron plates) with new electric stove. With the old electric stove with cast iron plates, much more mass must be heated, so it consumes about 50% more electricity than a new electric stove. An induction stove consumes even less electricity (about 20% less) because it can heat much faster and cooking therefore takes less time (source FOCUS Online).
Cooling
- Use air conditioning as little as possible and do not set temperature too low. When it’s hot outside, it’s often enough to have a few degrees difference in your own four walls to make the temperature feel much more pleasant. In addition, the air conditioning dries the air, which makes the perceived temperature much more pleasant anyway. So it doesn’t always have to be American 18 degrees.
- Use fan instead of air conditioner. A fan Helps in severe heat, of course, less than air conditioning, but also consumes much less electricity and can still make the heat much more bearable.
Washing
- For dishwasher and washing machine, use economy program whenever possible. The only drawback: it takes longer.
- Run dishwasher, washing machine and clothes dryer as little as possible. So only if they are really full.
- Whenever possible, hang laundry outdoors or in the laundry room to dry. This also protects the textiles.
Further exciting and useful tools and information sources on the subject of saving electricity for you
Do you know your own electricity needs? Or are you aware of whether you use electricity sparingly or wastefully? Here you will find the best sources of information and tools to learn more about your electricity needs and electricity saving measures.
www.energiebox.ch
On this website you can easily find out how efficient your household is by means of a question-and-answer game. The quick test contains ten questions according to the multiple-choice principle and takes about 1 minute. The evaluation shows your savings potential and classifies your household into one of the 7 classes of the energy label.
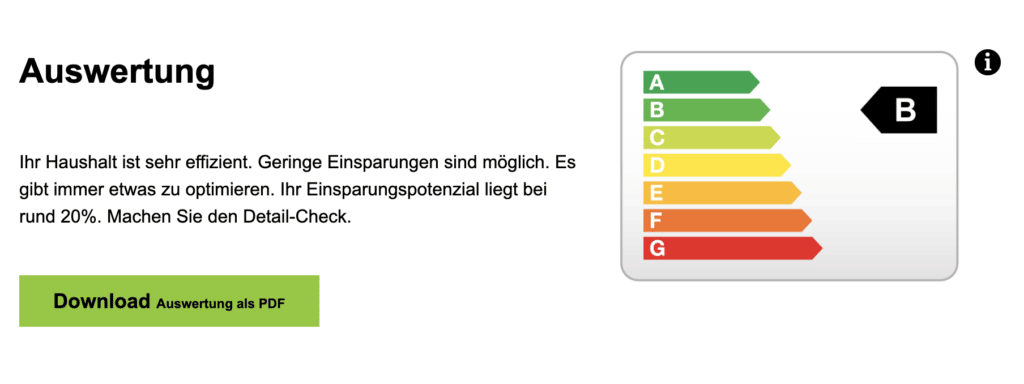
Energy label and efficiency requirements Federal Office of Energy
Here you can find detailed information about the energy labels of household appliances. These will help you choose economical electrical appliances.
energieswitzerland.ch
Informative website about energy saving. SwissEnergy provides extensive information for private individuals and companies on household appliances and the efficient use of energy.

Conclusion: knowing the power consumption of devices definitely helps to save electricity
Saving electricity can quickly be associated with doing without and restrictions in everyday life. But it doesn’t have to be.
Taking a brief look at the most important facts and figures on the subject of electricity consumption is one of the best steps you can take in the right direction to reduce your electricity consumption without making major sacrifices.
Now that you know the biggest power guzzlers in your household, it will be much easier for you to make the right decision the next time you press the ON button. And at the end of the year you will be surprised with a lower electricity bill.
Disclaimer
This article is not a scientific paper. We are aware that many assumptions and simplifications have been made regarding performance and power consumption. The aim of the article is to give the reader an overview and a sense of the power consumption of different electrical appliances in the home to help him save electricity. The information was compiled from various sources with the aim of summarizing the most important facts about electricity consumption in a comprehensible way. Without claim to completeness.




